Health
New RNA Molecule Discovered Could Combat Neurodegenerative Diseases
Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis and the University of California have identified a newly discovered RNA molecule, named FAM151B-DT, which may play a crucial role in limiting the aggregation of proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases. Their findings, published in the journal Molecular Psychiatry, highlight the potential of this RNA as a target for treatment strategies aimed at conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
Neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia, involve the progressive loss of neurons and a subsequent decline in cognitive function. Previous research has linked these diseases to the accumulation of misfolded proteins, particularly tau and α-synuclein. Tau stabilizes microtubules within neurons, while α-synuclein is critical for regulating neurotransmitter release. The abnormal aggregation of these proteins is a hallmark of various neurodegenerative conditions, but the underlying mechanisms prompting their accumulation remain poorly understood.
In their study, the research team aimed to explore the role of FAM151B-DT in the aggregation of tau and α-synuclein proteins. “Neurodegenerative diseases share common features of protein aggregation along with other pleiotropic traits,” the authors noted, emphasizing the need for identifying key regulators of these traits.
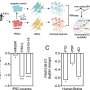
The researchers employed a combination of transcriptomics, mass spectrometry, and biochemical assays to analyze the role of this novel long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) in the pathophysiology of tau-related diseases. Their investigation included examining brain tissue samples from individuals diagnosed with neurodegenerative diseases and comparing them to samples from healthy individuals.
They found that FAM151B-DT levels were significantly reduced in brain tissues from patients with conditions like frontotemporal lobar dementia and progressive supranuclear palsy. “We show that silencing FAM151B-DT in vitro is sufficient to enhance tau and α-synuclein aggregation,” the authors explained. This indicates that the RNA molecule plays a vital role in maintaining protein homeostasis within neuronal cells.
The experimental approach involved growing stem cells in a laboratory setting and silencing the identified protein. The results revealed that this action led to increased aggregation of tau and α-synuclein, both of which are implicated in neuronal damage.
To further understand FAM151B-DT’s mechanism, the researchers characterized its interactions within the cell. They found that FAM151B-DT resides in the cytoplasm, where it interacts with tau, α-synuclein, and proteins involved in maintaining protein balance. When FAM151B-DT was silenced, it hindered autophagy, a crucial process for clearing aggregated proteins, resulting in the accumulation of tau and α-synuclein.
The implications of this study are significant, suggesting that FAM151B-DT is essential for regulating tau and α-synuclein levels in neurons. Its silencing appears to trigger the aggregation of proteins linked to neurodegenerative diseases, underscoring its potential as a therapeutic target. The authors concluded that increasing the expression of FAM151B-DT could facilitate autophagic clearance of phosphorylated tau and α-synuclein, thereby reducing their aggregation.
“Overall, these findings pave the way for further exploration of FAM151B-DT as a promising molecular target for several neurodegenerative diseases,” they stated. This discovery not only enhances the understanding of neurodegenerative conditions but also opens avenues for developing early treatment options or alleviating symptoms associated with these debilitating diseases.
The study’s authors, including Arun Renganathan and Miguel A. Minaya, have contributed significantly to advancing knowledge in this critical area of neuroscience. Their insights may lead to innovative therapeutic strategies in the future, offering hope for individuals affected by these challenging conditions.
-
 Science4 weeks ago
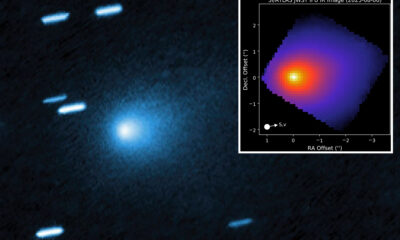
Science4 weeks agoInterstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Emits Unique Metal Alloy, Says Scientist
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoResearchers Achieve Fastest Genome Sequencing in Under Four Hours
-

 Politics4 weeks ago
Politics4 weeks agoAfghan Refugee Detained by ICE After Asylum Hearing in New York
-

 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks agoIconic Sand Dollar Social Club Listed for $3 Million in Folly Beach
-

 Health4 weeks ago
Health4 weeks agoPeptilogics Secures $78 Million to Combat Prosthetic Joint Infections
-

 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks agoMcEwen Inc. Secures Tartan Lake Gold Mine Through Acquisition
-

 Lifestyle4 weeks ago
Lifestyle4 weeks agoJump for Good: San Clemente Pier Fundraiser Allows Legal Leaps
-
 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoMars Observed: Detailed Imaging Reveals Dust Avalanche Dynamics
-

 Health4 weeks ago
Health4 weeks agoResearcher Uncovers Zika Virus Pathway to Placenta Using Nanotubes
-

 World4 weeks ago
World4 weeks agoUS Passport Ranks Drop Out of Top 10 for First Time Ever
-

 Entertainment4 weeks ago
Entertainment4 weeks agoJennifer Lopez Addresses A-Rod Split in Candid Interview
-

 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks agoSan Jose High-Rise Faces Foreclosure Over $182.5 Million Loan