Science
NASA Models Earth’s Life Span: Humans Face Sooner Deadline
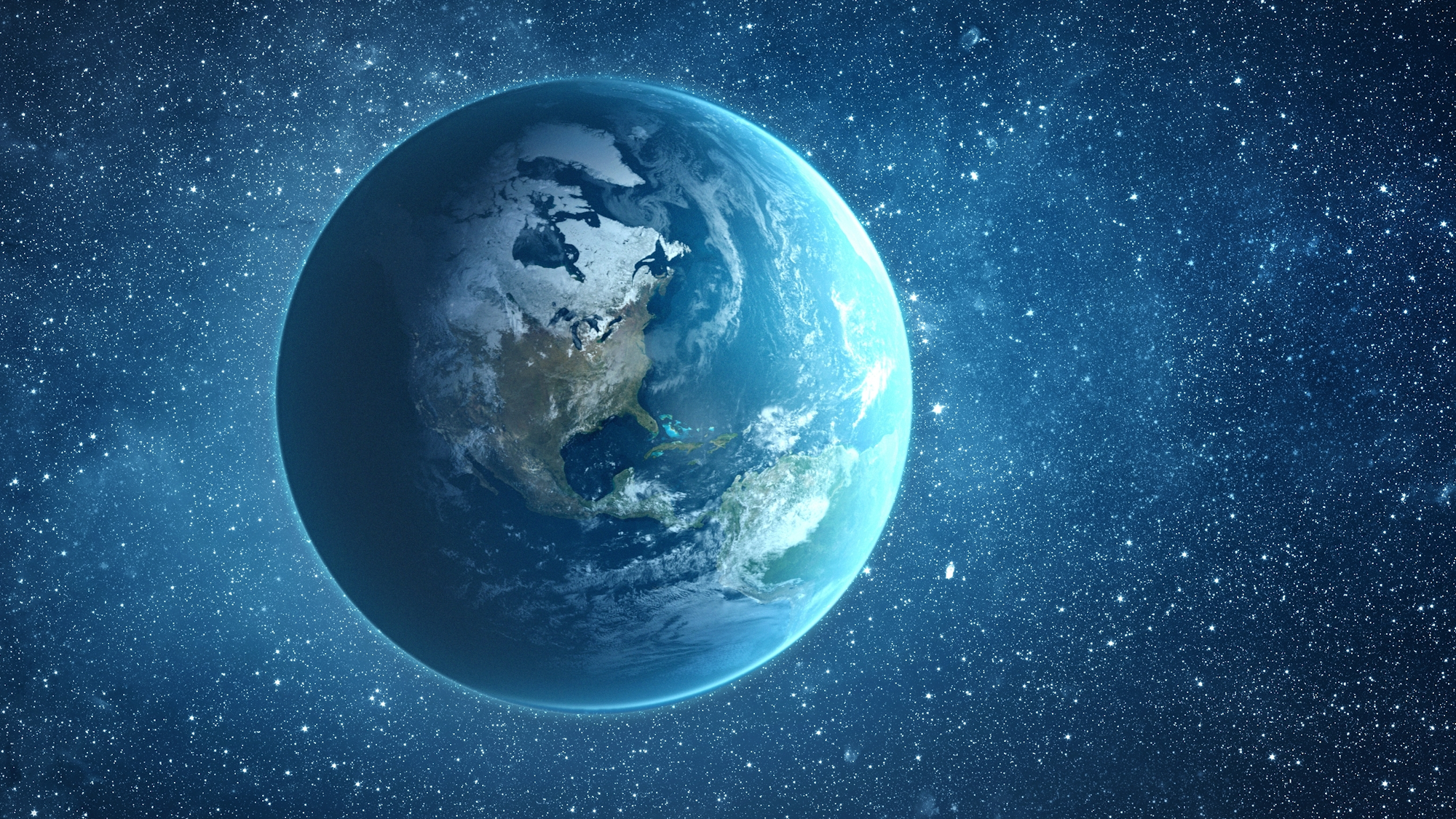

NASA, in collaboration with researchers from Toho University in Japan, has utilized advanced supercomputers to project the future of life on Earth. The findings indicate that while life on our planet is expected to persist for billions of years, the potential end for humans may arrive much sooner than previously anticipated.
The research highlights that the ultimate fate of all life on Earth is closely tied to the lifespan of the sun. In approximately 1,000,002,021, the sun will reach a stage where its increasing heat makes Earth inhospitable. At that point, even the most resilient organisms will struggle to survive under extreme surface conditions.
As the sun continues to warm, significant changes in Earth’s atmosphere will occur, resulting in declining oxygen levels and deteriorating air quality. These predictions stem from a detailed climate model that takes into account solar radiation and its effects. Current signs, such as intensified coronal mass ejections and solar storms, are already influencing the Earth’s magnetic field and diminishing oxygen levels, providing researchers with insights into potential long-term outcomes.
While no precise date is available for the end of human life, the researchers caution that environmental conditions could become untenable much sooner than the billion-year timeline. The ongoing effects of human-induced climate change are accelerating these challenges, as evidenced by rising global temperatures and the rapid melting of polar ice.
Preparing for an Uncertain Future
The decline of life on Earth will be gradual rather than abrupt. Despite the long timeline, researchers emphasize the necessity of proactive measures for humanity’s future. Some scientists advocate for technological solutions, such as closed life support systems and artificial habitats, to extend habitable environments for as long as possible.
Additionally, there are ambitious plans to explore long-term space colonization. Missions to Mars, led by organizations like NASA and SpaceX, are being considered as viable strategies for ensuring the survival of human life beyond Earth.
As the scientific community continues to investigate these pressing issues, the focus remains on understanding and mitigating the impacts of climate change while exploring new frontiers in space. The future may hold unforeseen challenges, but preparation and innovation could play a crucial role in sustaining humanity.
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Leads $25M AI Project to Monitor Natural Disasters
-
 Science2 months ago
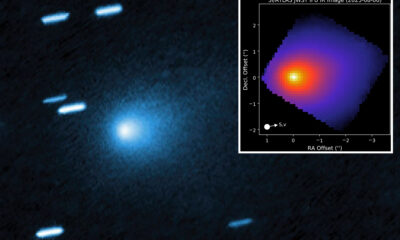
Science2 months agoInterstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Emits Unique Metal Alloy, Says Scientist
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoResearchers Achieve Fastest Genome Sequencing in Under Four Hours
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoIconic Sand Dollar Social Club Listed for $3 Million in Folly Beach
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoAfghan Refugee Detained by ICE After Asylum Hearing in New York
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoMcEwen Inc. Secures Tartan Lake Gold Mine Through Acquisition
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoPeptilogics Secures $78 Million to Combat Prosthetic Joint Infections
-
 Science2 months ago
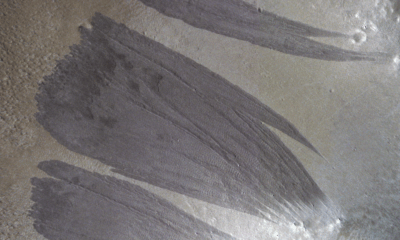
Science2 months agoMars Observed: Detailed Imaging Reveals Dust Avalanche Dynamics
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoJump for Good: San Clemente Pier Fundraiser Allows Legal Leaps
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoResearcher Uncovers Zika Virus Pathway to Placenta Using Nanotubes
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoJennifer Lopez Addresses A-Rod Split in Candid Interview
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoUS Passport Ranks Drop Out of Top 10 for First Time Ever