Health
First Documented Death from Alpha-Gal Syndrome Raises Alarm
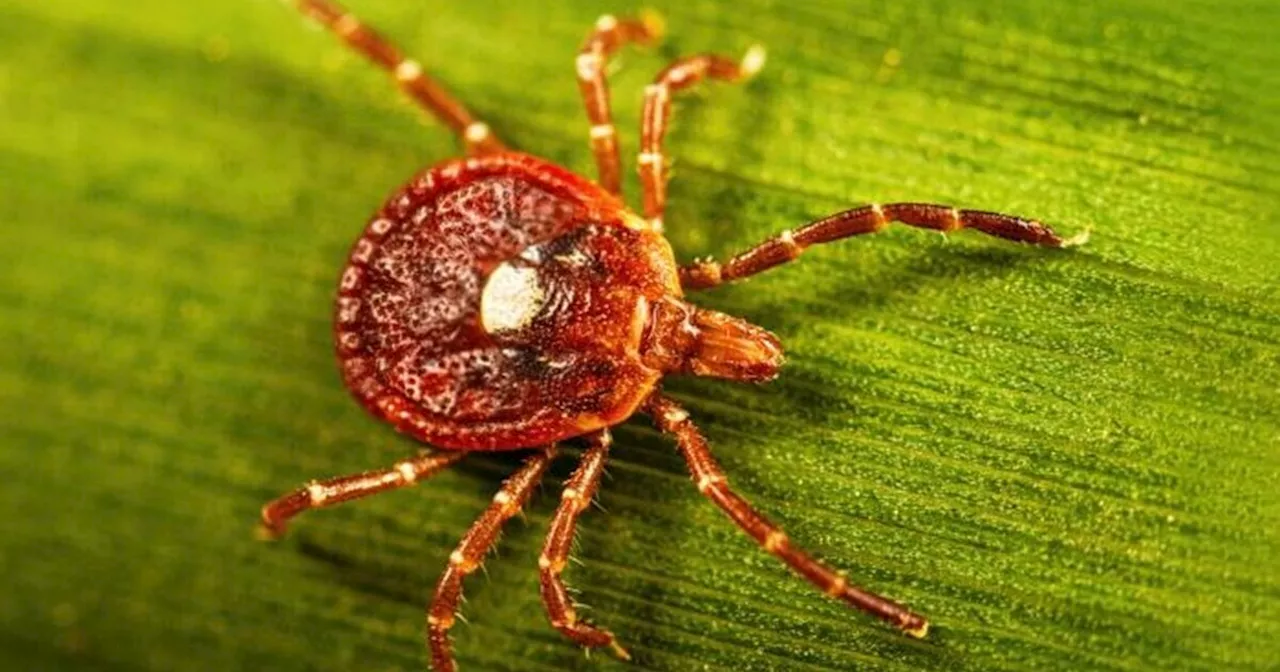

Researchers have reported the first documented death attributed to alpha-gal syndrome, a serious allergic reaction to red meat linked to bites from the lone star tick. The case involves a 47-year-old pilot from New Jersey, who died after consuming a hamburger at a barbecue in 2024. This tragic incident highlights the increasing severity of tick-borne illnesses and raises significant concerns about public health.
The pilot began feeling ill approximately four hours after eating the hamburger. His son found him unconscious in a bathroom, surrounded by vomit. Despite immediate medical attention, he was pronounced dead upon arrival at the hospital. An autopsy revealed that the cause of death was a sudden unexplained event, emphasizing the unpredictable and severe nature of alpha-gal syndrome.
The pilot’s wife revealed that he had experienced gastrointestinal symptoms, including abdominal discomfort, nausea, and diarrhea after consuming red meat in the past. Initially mistaken for food poisoning, these symptoms were never linked to a serious allergic condition. This case demonstrates the challenges in recognizing and diagnosing alpha-gal syndrome, particularly in individuals who have not previously been diagnosed.
Understanding Alpha-Gal Syndrome
Alpha-gal syndrome is characterized by an allergic reaction to alpha-gal, a sugar molecule found in red meat. Following a bite from a lone star tick, the body may develop an immune response to this sugar, triggering severe allergic reactions upon consumption of red meat. In this pilot’s case, multiple bites from lone star ticks, thought to be mistaken for chigger bites, likely contributed to the development of the allergy.
A blood sample taken post-mortem confirmed evidence of an allergic reaction to alpha-gal, underscoring the need for increased awareness among both the public and healthcare providers. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the number of identified cases of alpha-gal syndrome has significantly increased in recent years. Estimates suggest that as many as 450,000 people may be affected, indicating that many cases remain undiagnosed.
Experts attribute the rise in alpha-gal syndrome to the increasing population of lone star ticks, which are now found in more regions due to climate change and shifts in habitat. The CDC emphasizes the need for proactive measures to prevent tick bites, such as using insect repellent, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding areas where ticks are prevalent.
The Importance of Awareness and Early Diagnosis
The pilot’s experience serves as a stark reminder of the potential severity of alpha-gal syndrome. Experts recommend that individuals experiencing unexplained gastrointestinal symptoms, such as diarrhea and abdominal pain, consider testing for this condition. The American Gastroenterological Association advocates for greater awareness and prompt diagnosis to mitigate the risks associated with the allergy.
Currently, there is no vaccine available for alpha-gal syndrome. The primary management strategy involves dietary modifications, specifically eliminating red meat from one’s diet. The increasing prevalence of lone star ticks further underscores the urgency of addressing this public health concern.
The pilot’s tragic death emphasizes the need for comprehensive education on alpha-gal syndrome, its symptoms, and management strategies. As cases of this allergy continue to rise, it is imperative for both the public and healthcare professionals to remain vigilant and informed about the risks associated with tick bites and the potential progression of tick-borne allergies.
-
 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoInterstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Emits Unique Metal Alloy, Says Scientist
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoResearchers Achieve Fastest Genome Sequencing in Under Four Hours
-

 Politics1 month ago
Politics1 month agoAfghan Refugee Detained by ICE After Asylum Hearing in New York
-

 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks agoIconic Sand Dollar Social Club Listed for $3 Million in Folly Beach
-

 Health1 month ago
Health1 month agoPeptilogics Secures $78 Million to Combat Prosthetic Joint Infections
-

 Business1 month ago
Business1 month agoMcEwen Inc. Secures Tartan Lake Gold Mine Through Acquisition
-

 Lifestyle1 month ago
Lifestyle1 month agoJump for Good: San Clemente Pier Fundraiser Allows Legal Leaps
-
 Science1 month ago
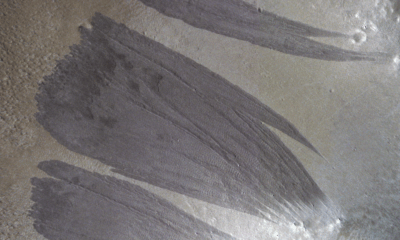
Science1 month agoMars Observed: Detailed Imaging Reveals Dust Avalanche Dynamics
-

 Health4 weeks ago
Health4 weeks agoResearcher Uncovers Zika Virus Pathway to Placenta Using Nanotubes
-

 World1 month ago
World1 month agoUS Passport Ranks Drop Out of Top 10 for First Time Ever
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoJennifer Lopez Addresses A-Rod Split in Candid Interview
-

 Business1 month ago
Business1 month agoSan Jose High-Rise Faces Foreclosure Over $182.5 Million Loan