Politics
Trump Expands Military Presence in Latin America Amid Rivalry with China

The United States is significantly increasing its military presence in the Caribbean, a move that many analysts view as an attempt to reclaim influence in Latin America. This strategy, spearheaded by President Donald Trump, includes targeted operations against alleged drug trafficking vessels in the Caribbean and eastern Pacific. Critics argue that these actions are less about combating drug-related crime and more about reinforcing U.S. dominance in the region.
In a recent statement, Peter Hegseth, Secretary of War, emphasized this intention by declaring, “With President Trump, we are going to reclaim our backyard.” This remark underscores a revival of the Monroe Doctrine, a 19th-century policy asserting U.S. authority over Latin America and warning European powers against interference. Originally articulated in 1823, the doctrine has been a cornerstone of U.S. foreign policy, aiming to establish a clear sphere of influence in the region.
The current developments reflect an evolution in U.S. imperial strategy, particularly in response to the rising influence of China. As China solidifies its role as a major trading partner in South America, with trade reaching approximately £393 billion in 2024, the U.S. is compelled to reassess its approach. This shift has involved a departure from the post-World War II strategy centered on a liberal capitalist order and institutions like the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund.
Historically, U.S. intervention in Latin America has been marked by military actions and support for regimes favorable to U.S. interests. From 1898 to 1994, the U.S. engaged in 41 interventions, often resulting in violence and upheaval. Notable examples include the U.S.-backed coup in Chile in 1973 that ousted democratically elected President Salvador Allende, leading to the authoritarian regime of Augusto Pinochet, which resulted in over 3,000 fatalities and widespread human rights abuses.
The recent increase in U.S. military operations is also linked to ongoing tensions with China. The U.S. has become increasingly aware that its declining influence in various parts of the world, particularly following military setbacks in Iraq and Afghanistan, has opened opportunities for China. As China invests heavily in Latin American resources—particularly in lithium extraction, where it has committed over £8.3 billion since 2018—the U.S. aims to counteract this influence.
In a bid to maintain control, the Trump administration has imposed economic sanctions on several Latin American countries and has shown support for far-right governments. For example, high tariffs were placed on Brazil following the conviction of former President Jair Bolsonaro, while a currency swap worth £15.2 billion was extended to Argentinian President Javier Milei. These actions reflect a strategy of aligning with local leaders who share U.S. interests.
Venezuela has emerged as a focal point in this renewed U.S. strategy. The country, rich in oil reserves, presents a critical target for U.S. interests, particularly as Chinese investments in Venezuelan oil production grow. In September 2024, China began operating its first oil platform in the country, indicating its deepening involvement. The U.S. aims to gain control over Venezuela’s oil wealth, not for domestic use, but to prevent Chinese access and maintain its strategic advantage.
As tensions escalate, Trump has issued threats regarding the potential takeover of the Panama Canal, a vital trade route. His administration’s rhetoric suggests a willingness to use military force to secure U.S. interests in the region. The historical context of U.S. interventions raises concerns about the potential for violence and unrest as the U.S. seeks to reassert its dominance.
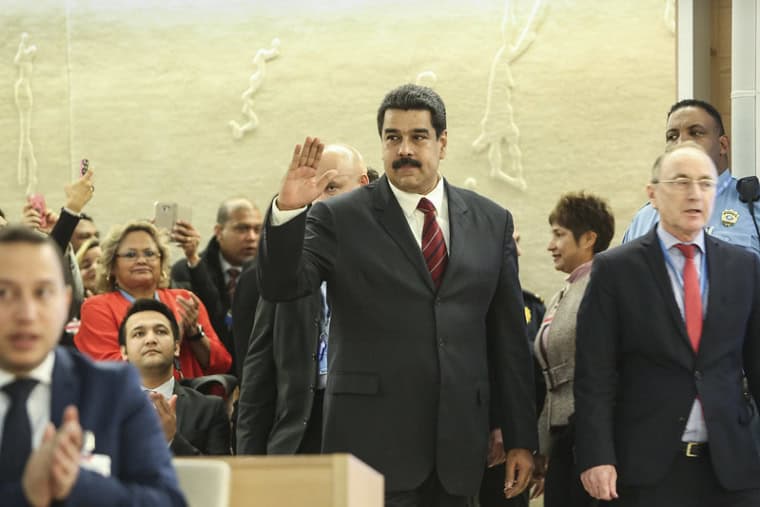
The situation in Venezuela is particularly complex. President Nicolás Maduro, facing international criticism and internal dissent, has been accused of corruption and authoritarianism. Despite claiming to uphold the legacy of the Bolivarian Revolution initiated by Hugo Chavez, Maduro’s government has alienated many citizens, leading to widespread disillusionment and a decline in support. The U.S. has expressed a clear intention to remove Maduro from power, offering a £38 million bounty for his capture.
While there is strong resistance to U.S. imperialism within Venezuela and across Latin America, the struggle for power remains fraught with challenges. Historical attempts to engineer regime change have often resulted in catastrophic consequences. The need for local movements to mobilize against both the corrupt ruling classes and foreign intervention is crucial for the future of the region.
In summary, the U.S.’s renewed focus on Latin America under the Trump administration signals an aggressive strategy to counter China’s growing influence and reassert its historical dominance. The implications of these actions remain to be seen, but the potential for conflict and instability is significant as both nations vie for control over this geopolitically important region.
-
 Science4 weeks ago
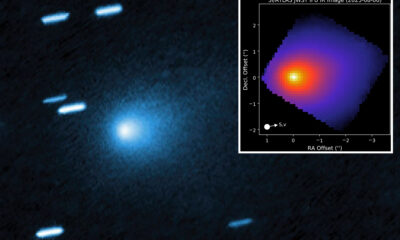
Science4 weeks agoInterstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Emits Unique Metal Alloy, Says Scientist
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoResearchers Achieve Fastest Genome Sequencing in Under Four Hours
-

 Politics1 month ago
Politics1 month agoAfghan Refugee Detained by ICE After Asylum Hearing in New York
-

 Business1 month ago
Business1 month agoIconic Sand Dollar Social Club Listed for $3 Million in Folly Beach
-

 Health1 month ago
Health1 month agoPeptilogics Secures $78 Million to Combat Prosthetic Joint Infections
-

 Business1 month ago
Business1 month agoMcEwen Inc. Secures Tartan Lake Gold Mine Through Acquisition
-

 Lifestyle1 month ago
Lifestyle1 month agoJump for Good: San Clemente Pier Fundraiser Allows Legal Leaps
-
 Science1 month ago
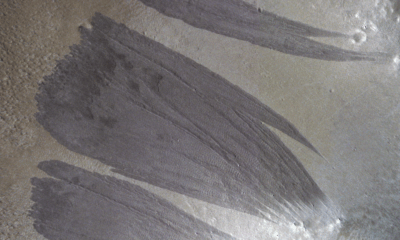
Science1 month agoMars Observed: Detailed Imaging Reveals Dust Avalanche Dynamics
-

 Health1 month ago
Health1 month agoResearcher Uncovers Zika Virus Pathway to Placenta Using Nanotubes
-

 World1 month ago
World1 month agoUS Passport Ranks Drop Out of Top 10 for First Time Ever
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoJennifer Lopez Addresses A-Rod Split in Candid Interview
-

 Business1 month ago
Business1 month agoSan Jose High-Rise Faces Foreclosure Over $182.5 Million Loan