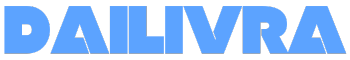Health
Genetic Insights Reveal Suicide Risk Linked to Early Depression

A recent study published in Nature Genetics has unveiled significant findings regarding the hereditary aspects of depression and its association with suicide risk. Researchers, including those from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden, discovered that depression arising in young adulthood is more strongly linked to genetic factors and presents a heightened risk of suicide attempts compared to depression that develops later in life.
The study highlights that individuals who experience depression during their formative years may carry genetic predispositions that increase their vulnerability to severe mental health challenges. This research underscores the necessity for early intervention and tailored treatment strategies for those affected.
Key Findings on Hereditary Links
The researchers analyzed data from various sources, focusing on genetic markers associated with depression. The results indicated that the heritability of depression in young adults is approximately 30% to 50%, significantly higher than the heritability observed in individuals diagnosed in later life. This genetic component is critical as it suggests that family history plays a vital role in understanding an individual’s mental health trajectory.
Moreover, the correlation between early-onset depression and suicide attempts is alarming. The study noted that young adults with a history of depression were over two times more likely to attempt suicide than their peers without such a history. These findings emphasize the importance of recognizing and addressing mental health issues at an early stage.
Implications for Mental Health Strategies
Given the robust link between genetics and the risk of suicide in young adults, mental health professionals may need to reconsider their approaches. The study advocates for enhanced screening processes in younger populations, especially for those with a family history of mental health disorders. By identifying at-risk individuals earlier, healthcare providers can implement preventive measures, potentially saving lives.
The researchers also stress the importance of integrating genetic testing into routine mental health assessments. Understanding an individual’s genetic predisposition could lead to personalized treatment plans, thereby improving outcomes for those struggling with depression.
In conclusion, this groundbreaking research from Karolinska Institutet offers invaluable insights into the genetic underpinnings of depression and its associated risks. As the understanding of these links deepens, it opens the door for more effective interventions, ultimately aiming to reduce the tragic outcomes associated with mental health disorders.
-
 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoInterstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Emits Unique Metal Alloy, Says Scientist
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoResearchers Achieve Fastest Genome Sequencing in Under Four Hours
-

 Politics4 weeks ago
Politics4 weeks agoAfghan Refugee Detained by ICE After Asylum Hearing in New York
-

 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks agoIconic Sand Dollar Social Club Listed for $3 Million in Folly Beach
-

 Health4 weeks ago
Health4 weeks agoPeptilogics Secures $78 Million to Combat Prosthetic Joint Infections
-

 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks agoMcEwen Inc. Secures Tartan Lake Gold Mine Through Acquisition
-

 Lifestyle4 weeks ago
Lifestyle4 weeks agoJump for Good: San Clemente Pier Fundraiser Allows Legal Leaps
-
 Science4 weeks ago
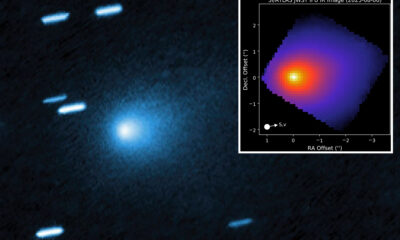
Science4 weeks agoMars Observed: Detailed Imaging Reveals Dust Avalanche Dynamics
-

 Health4 weeks ago
Health4 weeks agoResearcher Uncovers Zika Virus Pathway to Placenta Using Nanotubes
-

 World4 weeks ago
World4 weeks agoUS Passport Ranks Drop Out of Top 10 for First Time Ever
-

 Entertainment4 weeks ago
Entertainment4 weeks agoJennifer Lopez Addresses A-Rod Split in Candid Interview
-

 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks agoSan Jose High-Rise Faces Foreclosure Over $182.5 Million Loan