Health
Higher Lifetime Alcohol Consumption Raises Colorectal Cancer Risk

Research has established a clear connection between alcohol consumption and an increased risk of colorectal cancer. A recent study published in 2023 emphasizes that individuals with higher lifetime alcohol consumption face a significantly elevated risk, particularly for rectal cancer. Importantly, the findings indicate that ceasing alcohol intake can effectively reduce this risk.
The study, conducted by a team of researchers at a leading health institution, analyzed data from thousands of participants over several years. The results revealed that individuals who consumed alcohol excessively throughout their lives exhibited a marked increase in colorectal cancer cases. This correlation underscores the importance of understanding the long-term health implications of alcohol consumption.
Details of the Study
The research assessed the drinking habits of participants and categorized them based on their alcohol intake levels. Those who engaged in heavy drinking were found to have a 70% higher likelihood of developing rectal cancer compared to non-drinkers. This statistic highlights a pressing public health concern, as colorectal cancer remains one of the most prevalent cancers globally.
In addition to the immediate findings, the study also focused on the impacts of quitting alcohol. Participants who stopped drinking reported a significant decline in their cancer risk over time. This aspect of the research provides a positive outlook for those seeking to improve their long-term health by making lifestyle changes.
Implications for Public Health
Health organizations worldwide are likely to take note of these findings as they continue to educate the public on the risks associated with alcohol consumption. The link between alcohol and colorectal cancer adds to the growing body of evidence urging individuals to moderate their drinking habits.
According to the World Health Organization, alcohol is a significant risk factor for various cancers, and the implications of this study could drive further initiatives aimed at reducing alcohol consumption in populations globally.
Moreover, the findings support existing guidelines that recommend limiting alcohol intake to minimize health risks. With colorectal cancer being one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths, this research emphasizes the need for ongoing awareness and preventive measures in public health campaigns.
In conclusion, the association between higher lifetime alcohol consumption and increased colorectal cancer risk sheds light on a critical health issue. As awareness grows, individuals are encouraged to consider the long-term effects of their drinking habits and the benefits of quitting alcohol. Continued research will be essential in further understanding this relationship and in shaping effective health policies.
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoSend Holiday Parcels for £1.99 with New Comparison Service
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Leads $25M AI Project to Monitor Natural Disasters
-
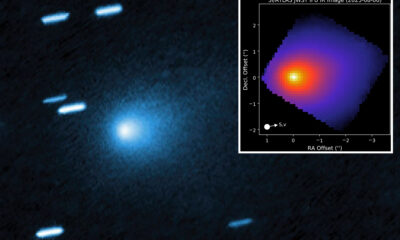
 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoInterstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Emits Unique Metal Alloy, Says Scientist
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoMaui County Reopens Upgraded Lānaʻi Fifth Street Courts Today!
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKelly McCreary Discusses Future of Maggie and Winston in Grey’s Anatomy
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoResearchers Achieve Fastest Genome Sequencing in Under Four Hours
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoIconic Sand Dollar Social Club Listed for $3 Million in Folly Beach
-

 Politics4 months ago
Politics4 months agoAfghan Refugee Detained by ICE After Asylum Hearing in New York
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoPeptilogics Secures $78 Million to Combat Prosthetic Joint Infections
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoMcEwen Inc. Secures Tartan Lake Gold Mine Through Acquisition
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoJump for Good: San Clemente Pier Fundraiser Allows Legal Leaps
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoResearcher Uncovers Zika Virus Pathway to Placenta Using Nanotubes