Health
New Approaches Combat Rising Myopia Rates in Young People

A growing body of evidence suggests that innovative strategies are making strides in slowing the progression of myopia among children and adolescents. By the year 2050, projections indicate that approximately 50% of the global population will be affected by nearsightedness, with nearly one billion individuals expected to experience severe forms of this condition.
To address this urgent health concern, Langis Michaud, a prominent researcher in the field, is conducting an extensive review of existing medical literature related to myopia. His work aims to consolidate findings that could inform future interventions designed to mitigate this escalating issue.
Understanding Myopia and Its Impact
Myopia, commonly known as nearsightedness, occurs when the eye grows too long, causing distant objects to appear blurry. It has become a significant public health challenge, particularly among younger populations. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the rise in myopia can be attributed to a combination of genetic predispositions and environmental factors, such as increased screen time and reduced outdoor activity.
Michaud’s research highlights various strategies that have shown promise in slowing myopia progression. Interventions like specialized contact lenses, orthokeratology (a procedure using rigid contact lenses to reshape the cornea), and increased outdoor exposure have been recognized for their potential effectiveness. These approaches aim not only to improve visual acuity but also to alter the underlying biological changes in the eye that contribute to myopia.
Global Trends and Future Directions
The alarming statistics surrounding myopia necessitate immediate action from health professionals and policymakers. Countries such as Singapore and South Korea are already witnessing a surge in myopia rates among children, prompting governments to allocate resources towards preventive strategies.
Michaud’s review serves as a critical resource for understanding the scope of myopia and the effectiveness of various interventions. He emphasizes the need for comprehensive public health initiatives that incorporate education about myopia prevention and management.
In light of these findings, it is crucial for families and educators to recognize the importance of outdoor activities and limit screen time for children. By fostering an environment that encourages healthy visual habits, communities can play a vital role in combating the myopia epidemic.
As research continues to evolve, Michaud urges collaboration among eye care professionals, researchers, and public health officials to implement effective strategies. The concerted effort could significantly reduce the burden of myopia and enhance the quality of life for future generations.
The upward trend in myopia prevalence is a call to action for global health systems. By investing in research and education today, we can pave the way for healthier eyes tomorrow.
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoSend Holiday Parcels for £1.99 with New Comparison Service
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Leads $25M AI Project to Monitor Natural Disasters
-
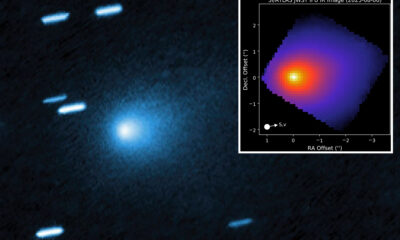
 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoInterstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Emits Unique Metal Alloy, Says Scientist
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoMaui County Reopens Upgraded Lānaʻi Fifth Street Courts Today!
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKelly McCreary Discusses Future of Maggie and Winston in Grey’s Anatomy
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoResearchers Achieve Fastest Genome Sequencing in Under Four Hours
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoIconic Sand Dollar Social Club Listed for $3 Million in Folly Beach
-

 Politics4 months ago
Politics4 months agoAfghan Refugee Detained by ICE After Asylum Hearing in New York
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoMcEwen Inc. Secures Tartan Lake Gold Mine Through Acquisition
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoPeptilogics Secures $78 Million to Combat Prosthetic Joint Infections
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoJump for Good: San Clemente Pier Fundraiser Allows Legal Leaps
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoResearcher Uncovers Zika Virus Pathway to Placenta Using Nanotubes