Health
New Enzyme Shows Promise in Treating Autoimmune Diseases
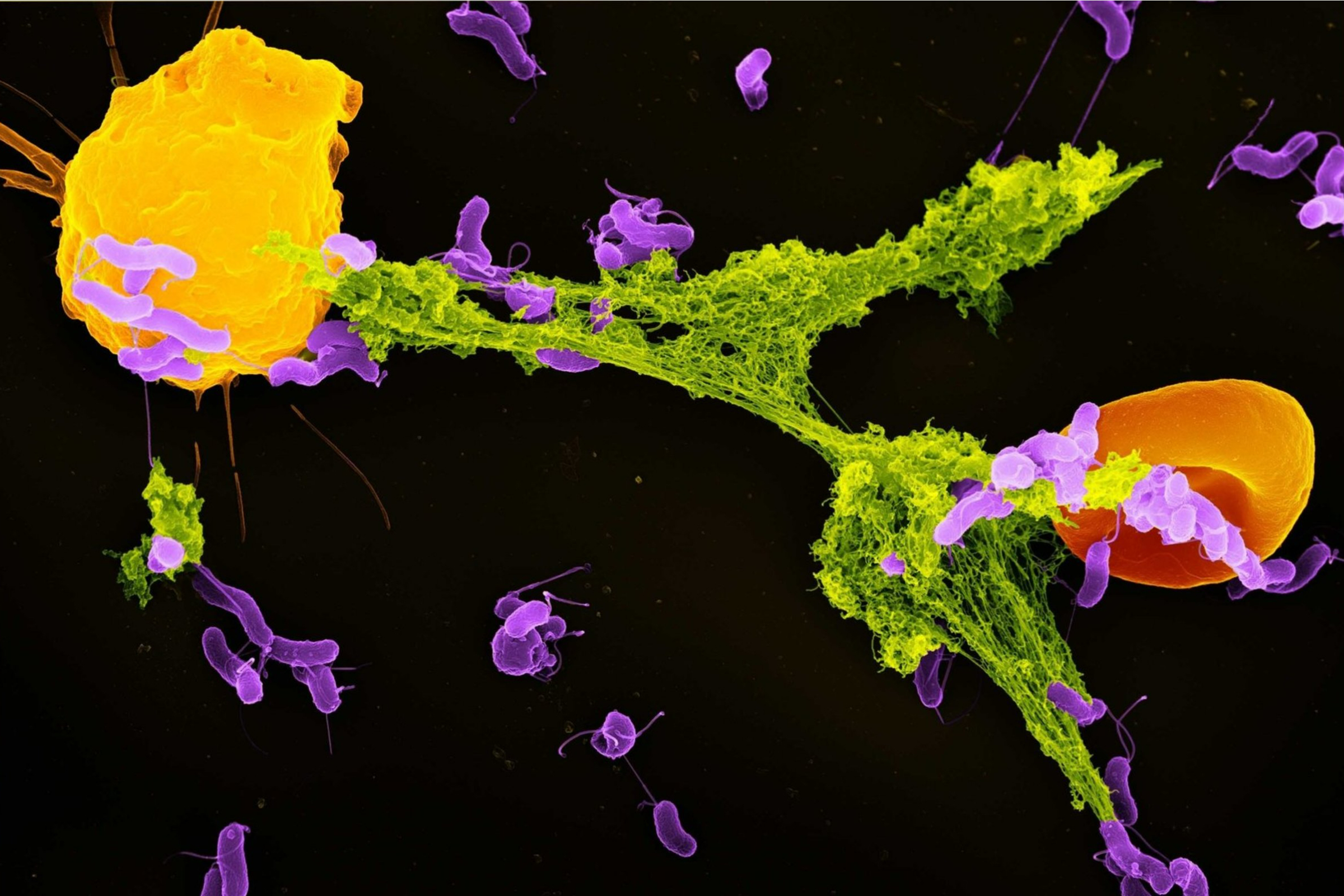
Research from Neutrolis suggests that a novel DNA-chopping enzyme could provide a new approach to combat autoimmune diseases. This early data highlights the potential of targeting neutrophils, a critical component of the immune system, in developing innovative treatments.
Neutrophils are white blood cells that play a vital role in the body’s first line of defense against infections. They are unique in that they can eject their DNA to form structures known as neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). These web-like formations ensnare and neutralize pathogens, but they can also contribute to inflammation and tissue damage when released excessively, as seen in various autoimmune conditions.
The enzyme studied by Neutrolis has demonstrated the ability to break down these NETs, potentially reducing their harmful effects. This mechanism could pave the way for therapies aimed at managing autoimmune diseases, where the immune system erroneously attacks the body’s own tissues.
According to a statement from Neutrolis, the enzyme’s ability to modulate immune responses presents a promising avenue for treatment. Early trials have shown that by reducing the formation of NETs, symptoms associated with autoimmune diseases may improve significantly.
Understanding the Impact of NETs on Autoimmune Diseases
In autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, the overproduction of NETs can exacerbate inflammation and lead to further health complications. By targeting and dismantling these structures, the enzyme could potentially minimize the damage caused by the immune system’s malfunction.
Neutrolis is currently planning further studies to explore the full range of the enzyme’s capabilities. Researchers are optimistic that these investigations will uncover additional benefits, potentially leading to more effective treatments for patients suffering from these debilitating conditions.
The implications of this research extend beyond just one class of diseases. If successful, therapies based on this enzyme might also be adapted for use in other inflammatory conditions, broadening the impact of Neutrolis’s findings.
As the company moves forward, it will be crucial for them to collaborate with healthcare professionals and researchers in the field to ensure that the development of therapeutic applications is grounded in rigorous scientific evaluation.
In summary, the discovery of this DNA-chopping enzyme represents a significant advancement in our understanding of the immune system’s complexities. Through ongoing research, Neutrolis aims to unlock new possibilities in the fight against autoimmune diseases, offering hope to millions affected by these often-challenging conditions.
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoIconic Sand Dollar Social Club Listed for $3 Million in Folly Beach
-

 Politics2 weeks ago
Politics2 weeks agoAfghan Refugee Detained by ICE After Asylum Hearing in New York
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoPeptilogics Secures $78 Million to Combat Prosthetic Joint Infections
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoResearchers Achieve Fastest Genome Sequencing in Under Four Hours
-

 Lifestyle2 weeks ago
Lifestyle2 weeks agoJump for Good: San Clemente Pier Fundraiser Allows Legal Leaps
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoResearcher Uncovers Zika Virus Pathway to Placenta Using Nanotubes
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoUS Passport Ranks Drop Out of Top 10 for First Time Ever
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoSan Jose High-Rise Faces Foreclosure Over $182.5 Million Loan
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoRegional Pilots’ Salaries Surge to Six Figures in 2025
-
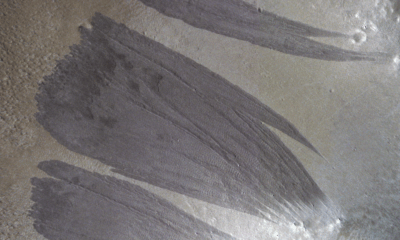
 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoMars Observed: Detailed Imaging Reveals Dust Avalanche Dynamics
-

 Entertainment2 weeks ago
Entertainment2 weeks agoJennifer Lopez Addresses A-Rod Split in Candid Interview
-

 Top Stories2 weeks ago
Top Stories2 weeks agoChicago Symphony Orchestra Dazzles with Berlioz Under Mäkelä