Science
Neanderthals, Orcas, and Cosmic Wonders: Science Headlines This Week

This week in science has unveiled significant findings regarding human evolution, animal behavior, and cosmic phenomena. Researchers have presented compelling evidence that Neanderthals were making fire as early as 400,000 years ago, while orcas and dolphins have been cooperating in their hunting strategies. Meanwhile, astronomical observations have revealed exciting developments in both our solar system and beyond, including the anticipated brightness of Jupiter and the imminent supernova of the star system V Sagittae.
Neanderthals’ Early Mastery of Fire
A new study has established that Neanderthals were capable of creating and controlling fire much earlier than previously believed. Archaeologists discovered evidence in Suffolk, England, indicating that these ancient humans were using fire around 400,000 years ago. This finding pushes back the timeline by approximately 350,000 years.
The presence of pyrite, a mineral known for producing sparks when struck against flint, at the site suggests that Neanderthals intentionally brought it to create fire. This finding supports ongoing debates among paleoanthropologists regarding the social and cultural implications of fire use among Neanderthals, which marked a key moment in human evolution.
Cooperative Hunting Between Orcas and Dolphins
In a fascinating development off the coast of British Columbia, a recent study has documented a rare partnership between northern resident killer whales (orcas) and Pacific white-sided dolphins. Observations show these two species working together while hunting for salmon, sharing the spoils of their kills.
The study claims this behavior represents the first documented instance of cooperative hunting and prey-sharing between these species. However, some experts argue that the interaction may not signify true cooperation but could instead reflect a behavior known as kleptoparasitism, where one species steals food from another.
Astronomical Events Light Up the Skies
In addition to these terrestrial discoveries, significant astronomical events are set to capture the attention of skywatchers. The binary star system V Sagittae is expected to illuminate the night sky with brilliant flares, potentially becoming visible from Earth within the next century as it approaches a supernova phase. These flares will be observable with the naked eye at any time of day.
This month also marks the appearance of Jupiter in the night sky, prompting some to ponder its connection to the biblical Star of Bethlehem. While the correlation remains speculative, the visibility of the planet is a highlight for astronomy enthusiasts.
Meanwhile, a particle detector located in South Dakota has yielded no evidence of dark matter, a key component of the universe’s structure. This investigation aimed to identify particles believed to constitute dark matter, but the latest findings have ruled out previous anomalies observed in earlier experiments.
Exploring Historical Frontiers
Shifting to archaeological news, recent discoveries at the historic fort of Vindolanda near Hadrian’s Wall are reshaping our understanding of life at the northern border of the Roman Empire. These findings suggest that the Roman frontier was not merely a militarized zone but a vibrant community reflecting the diverse demographics of the empire.
As the Roman Empire expanded, the 73-mile-long Hadrian’s Wall served as a critical barrier for nearly 300 years. The new evidence from Vindolanda sheds light on the daily lives and interactions of people living on the edge of this ancient superpower.
In addition to these significant findings, other scientific advancements have been reported, including a CDC panel’s vote to end recommendations for universal hepatitis B vaccination in newborns and new research indicating that 2024 may be the hottest year on record for the Arab region.
This week in science not only highlights groundbreaking discoveries but also emphasizes the interconnectedness of our past, present, and future, whether through ancient human behaviors, the cooperation of species, or the wonders of the universe.
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Leads $25M AI Project to Monitor Natural Disasters
-
 Science2 months ago
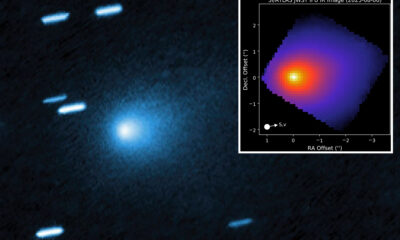
Science2 months agoInterstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Emits Unique Metal Alloy, Says Scientist
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoResearchers Achieve Fastest Genome Sequencing in Under Four Hours
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoIconic Sand Dollar Social Club Listed for $3 Million in Folly Beach
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoAfghan Refugee Detained by ICE After Asylum Hearing in New York
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoMcEwen Inc. Secures Tartan Lake Gold Mine Through Acquisition
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoPeptilogics Secures $78 Million to Combat Prosthetic Joint Infections
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoJump for Good: San Clemente Pier Fundraiser Allows Legal Leaps
-
 Science2 months ago
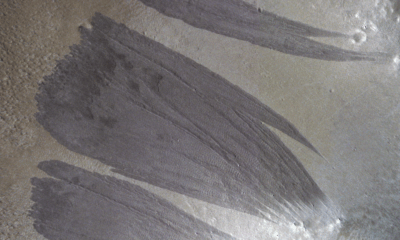
Science2 months agoMars Observed: Detailed Imaging Reveals Dust Avalanche Dynamics
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoResearcher Uncovers Zika Virus Pathway to Placenta Using Nanotubes
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoJennifer Lopez Addresses A-Rod Split in Candid Interview
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoUS Passport Ranks Drop Out of Top 10 for First Time Ever