Science
Study Reveals Ozempic’s Surprising Impact on Alcohol Consumption
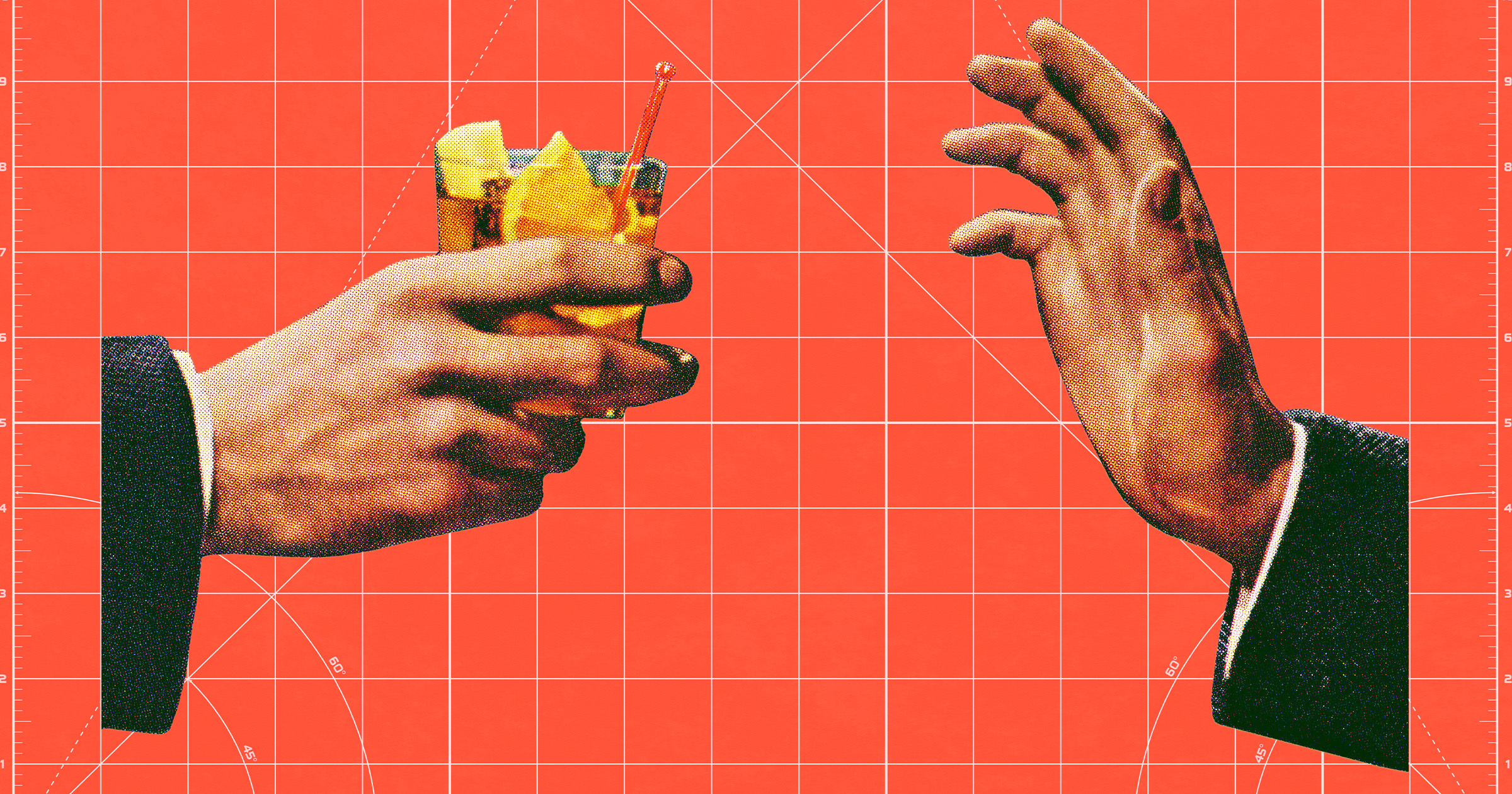
Recent research highlights an unexpected effect of GLP-1 medications, particularly the diabetes drug Ozempic, which may influence alcohol consumption among users. Originally developed to manage diabetes, semaglutide, the active ingredient in Ozempic and its counterpart Wegovy, has gained attention for its weight-loss benefits. Users report a reduced desire to consume alcohol after starting treatment, prompting investigations into the drug’s effects on cravings and addiction.
A study published in the journal Scientific Reports by researchers from Virginia Tech sheds light on how GLP-1 drugs may alter the body’s processing of alcohol. In this study, participants consumed three alcoholic beverages over one hour while researchers monitored their blood alcohol levels, glucose, and vital signs. The results indicated that those on GLP-1 medications felt less intoxicated compared to non-users, with their blood alcohol levels rising more gradually.
This delayed and diminished effect of alcohol is likely due to the known function of GLP-1 drugs, which slow gastric emptying. As a result, alcohol enters the bloodstream more slowly, potentially reducing its impact. The study suggests a dual effect: while GLP-1s may modify the neurological reward associated with alcohol, they also alter digestive processing.
According to Alex DiFeliceantonio, a neuroscientist at Virginia Tech involved in the research, understanding these interactions is crucial. He stated, “Faster-acting drugs have a higher abuse potential. They have a different impact on the brain. So if GLP-1s slow alcohol entering the bloodstream, they could reduce the effects of alcohol and help people drink less.”
Despite the promising findings, the study’s small sample size of just 20 participants calls for further research to confirm these effects and their implications for addiction treatment. The nuances of how GLP-1 drugs affect both the brain’s reward system and physical processes in the body present an ongoing area of exploration.
As this research progresses, it offers a glimpse into the potential of GLP-1 medications not only as weight-loss aids but also as tools for addressing substance use disorders. The interplay between medication, addiction, and the human body continues to unfold, promising new insights into effective treatment strategies.
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoIconic Sand Dollar Social Club Listed for $3 Million in Folly Beach
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoPeptilogics Secures $78 Million to Combat Prosthetic Joint Infections
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoAfghan Refugee Detained by ICE After Asylum Hearing in New York
-

 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoResearchers Achieve Fastest Genome Sequencing in Under Four Hours
-

 Lifestyle1 week ago
Lifestyle1 week agoJump for Good: San Clemente Pier Fundraiser Allows Legal Leaps
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoResearcher Uncovers Zika Virus Pathway to Placenta Using Nanotubes
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoUS Passport Ranks Drop Out of Top 10 for First Time Ever
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoRegional Pilots’ Salaries Surge to Six Figures in 2025
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoJennifer Lopez Addresses A-Rod Split in Candid Interview
-

 Top Stories6 days ago
Top Stories6 days agoChicago Symphony Orchestra Dazzles with Berlioz Under Mäkelä
-
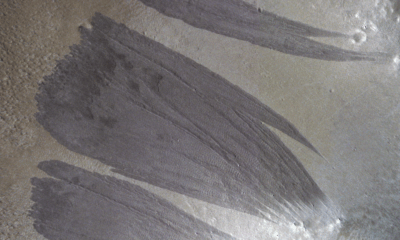
 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoMars Observed: Detailed Imaging Reveals Dust Avalanche Dynamics
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoObama Foundation Highlights Challenges in Hungary and Poland