Top Stories
Revolutionary S-Aquabots Unveiled for Eco-Friendly Monitoring
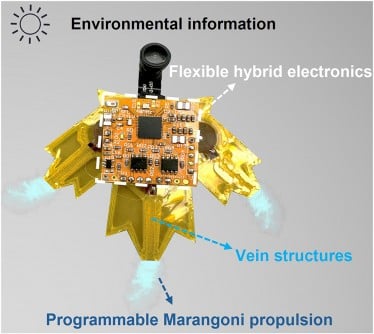
BREAKING NEWS: Researchers have just unveiled groundbreaking “S-aquabots” that promise to revolutionize environmental monitoring and aquatic robotics. Developed by teams from the University of Macau and Huazhong University of Science and Technology, these bio-inspired robots utilize innovative ethanol-fueled propulsion for enhanced mobility and adaptability, marking a significant leap forward in untethered aquatic technology.
The study, published in May 2025 in the journal eScience, reveals how these centimeter-scale robots harness the Marangoni effect—a principle observed in nature, specifically in water-striding beetles. Powered by a novel programmable Marangoni motor, the S-aquabots can navigate water surfaces silently and efficiently, achieving remarkable fuel efficiency that allows them to operate for up to 226 seconds on just 1.2 mL of ethanol.
Why does this matter NOW? With environmental challenges escalating globally, these aquabots provide a vital tool for real-time monitoring of water quality, pollution tracking, and ecological research without disturbing wildlife. Their silent operation, measured at 40 dB—comparable to natural background noise—ensures they can gather critical data unobtrusively.
The S-aquabots have demonstrated impressive capabilities including obstacle avoidance, pollutant collection, and the ability to execute preprogrammed movements, such as navigating a butterfly-shaped path using laser guidance. This level of control represents a transformative approach to aquatic robotics, enabling applications in search and rescue scenarios where precision is crucial.
Prof. Junwen Zhong, the study’s lead author, emphasized the innovative nature of these robots, stating,
“Our leaf-inspired S-aquabots demonstrate how biomimicry and advanced materials can overcome the long-standing challenges of aquatic robotics. The quiet motion and natural camouflage open possibilities for unobtrusive environmental monitoring.”
Looking ahead, these S-aquabots could be equipped with mini-cameras or sensors for extended environmental surveillance, tracking pollutants, or collecting weather data over long periods. The integration of sustainable energy sources, such as solar cells, is also on the horizon, potentially enhancing their operational endurance.
This technological breakthrough not only showcases the power of innovative design but also sets a new standard for eco-integrated robotic systems that can adapt to diverse aquatic environments. The implications for environmental protection and disaster response are significant, positioning these advanced robots as essential tools in the fight against pollution and climate change.
Stay tuned for more updates as this technology continues to evolve and finds its place in critical environmental initiatives worldwide. The future of responsive and responsible aquatic monitoring is here.
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoIconic Sand Dollar Social Club Listed for $3 Million in Folly Beach
-

 Politics2 weeks ago
Politics2 weeks agoAfghan Refugee Detained by ICE After Asylum Hearing in New York
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoPeptilogics Secures $78 Million to Combat Prosthetic Joint Infections
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoResearchers Achieve Fastest Genome Sequencing in Under Four Hours
-

 Lifestyle2 weeks ago
Lifestyle2 weeks agoJump for Good: San Clemente Pier Fundraiser Allows Legal Leaps
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoResearcher Uncovers Zika Virus Pathway to Placenta Using Nanotubes
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoUS Passport Ranks Drop Out of Top 10 for First Time Ever
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoSan Jose High-Rise Faces Foreclosure Over $182.5 Million Loan
-
 Science2 weeks ago
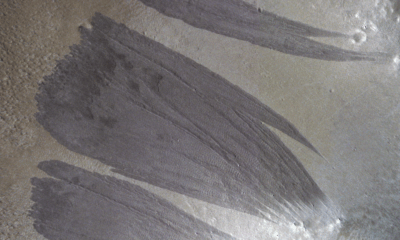
Science2 weeks agoMars Observed: Detailed Imaging Reveals Dust Avalanche Dynamics
-

 Entertainment2 weeks ago
Entertainment2 weeks agoJennifer Lopez Addresses A-Rod Split in Candid Interview
-

 Top Stories1 week ago
Top Stories1 week agoChicago Symphony Orchestra Dazzles with Berlioz Under Mäkelä
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoRegional Pilots’ Salaries Surge to Six Figures in 2025