Health
New Insights on T Cell Fate Reveal Asymmetric Division Role

Recent research has uncovered significant insights into the fate of T cells, a critical component of the immune system. The study reveals that during their division, T cells undergo a process called asymmetric cell division (ACD). This mechanism results in each daughter cell inheriting different cellular components, steering them towards distinct roles—one cell evolves into a short-lived effector T cell, while the other transitions into a long-lived memory T cell.
Understanding this process is vital for enhancing immunotherapy strategies, particularly in treating various diseases, including cancer. The differentiation between effector and memory T cells is not merely a matter of lifespan but also of function. Effector T cells are crucial for immediate responses against pathogens, while memory T cells provide long-term immunity, enabling the body to respond more swiftly to future infections.
The Role of Asymmetric Cell Division
The phenomenon of ACD is essential in generating diversity among T cells. During division, the unequal distribution of cellular components influences the developmental pathway each cell will follow. This research highlights the importance of these components, which include proteins and organelles that play roles in cell signaling and metabolic processes.
By studying the specific mechanisms involved in ACD, researchers aim to identify ways to manipulate these pathways. This could potentially improve the effectiveness of vaccines and therapeutic interventions by enhancing the generation of memory T cells.
The implications of this research extend beyond basic immunology. For instance, individuals receiving cancer immunotherapy could benefit from a better understanding of how to promote the formation of memory T cells. This could lead to longer-lasting protection against cancer recurrence following treatment.
Future Directions and Implications
The findings of this study provoke important questions about how T cell differentiation can be influenced. Researchers are exploring whether specific interventions could enhance the efficiency of ACD, thereby increasing the number of memory T cells produced during immune responses.
As scientists continue to investigate the intricate workings of T cells, the hope is to uncover additional strategies to bolster the immune system in combating diseases. This research stands as a testament to the complex interplay between cellular mechanics and immune function, offering promising avenues for future medical advancements.
With ongoing studies, the full potential of this research remains to be seen, but its foundational insights may one day contribute to transformative changes in how immunological therapies are approached globally.
-

 Lifestyle1 week ago
Lifestyle1 week agoSend Holiday Parcels for £1.99 with New Comparison Service
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Leads $25M AI Project to Monitor Natural Disasters
-
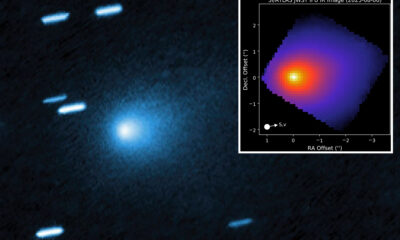
 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoInterstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Emits Unique Metal Alloy, Says Scientist
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoResearchers Achieve Fastest Genome Sequencing in Under Four Hours
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoIconic Sand Dollar Social Club Listed for $3 Million in Folly Beach
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoAfghan Refugee Detained by ICE After Asylum Hearing in New York
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoPeptilogics Secures $78 Million to Combat Prosthetic Joint Infections
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoMcEwen Inc. Secures Tartan Lake Gold Mine Through Acquisition
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoJump for Good: San Clemente Pier Fundraiser Allows Legal Leaps
-
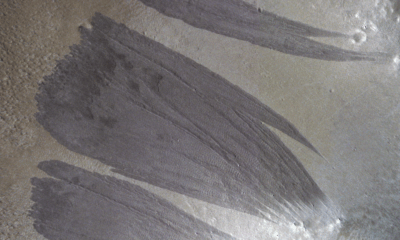
 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoMars Observed: Detailed Imaging Reveals Dust Avalanche Dynamics
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoResearcher Uncovers Zika Virus Pathway to Placenta Using Nanotubes
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoJennifer Lopez Addresses A-Rod Split in Candid Interview