Science
Scientists Discover Heat-Resistant Material from Meteorite Research

Recent research has unveiled a remarkable heat-resistant material derived from meteorites, potentially transforming the landscape of material science. Scientists investigating stony-iron meteorites have discovered a unique substance that can withstand extreme thermal conditions without compromising its structural integrity. This breakthrough could have significant implications for various industries on Earth.
A Window into the Cosmos
Meteorites are not just remnants of celestial history; they serve as valuable sources of information about the formation of our solar system. When these space rocks land on Earth, they carry with them insights into the conditions that shaped planets, asteroids, and other celestial bodies. Researchers have long studied meteorites to piece together our cosmic origins, but recent findings have taken this inquiry to new heights.
The focus of this study was on a specific class of meteorites known as stony-iron meteorites, which are composed of nearly equal parts metal and silicate. Through rigorous analysis employing advanced techniques such as scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction, scientists identified a material within these meteorites that exhibits extraordinary heat resistance. This material is distinguished by its unique molecular structure, which allows it to dissipate heat more effectively than conventional materials found on Earth.
Potential Transformations Across Industries
The discovery of this heat-defying material opens doors to innovative applications across several sectors. For instance, in aerospace engineering, spacecraft and satellites must endure extreme temperatures during launches and re-entries. Materials that maintain their properties under such conditions could enhance the safety and efficiency of space missions.
In the field of electronics, where managing heat is increasingly critical due to the demand for high-performance computing, this new material could be integrated into electronic components. Its ability to withstand heat may improve device performance and longevity, addressing a key challenge in modern technology.
Manufacturing processes involving high temperatures also stand to benefit. By utilizing materials that retain strength and efficiency under stress, industries could enhance their machinery and infrastructure. Furthermore, the energy sector, especially in renewable technologies like solar power and thermal storage, may experience improved performance by incorporating this heat-resistant material, potentially boosting energy conversion efficiencies.
While the implications of this discovery are promising, researchers caution that additional studies are needed. Understanding the full spectrum of this material’s properties, its scalability for production, and any potential environmental impacts will be crucial for transitioning this laboratory finding into practical applications.
The research has sparked renewed interest in meteorites as a source of novel materials. As advancements in materials science progress, the potential for discovering new substances from outer space continues to grow. These findings underscore the importance of ongoing exploration beyond our planet, as the cosmos may hold additional revolutionary materials waiting to be uncovered.
In summary, the identification of a heat-resistant material from meteorites not only enhances our understanding of cosmic phenomena but also paves the way for advancements in material science and engineering on Earth. As researchers delve deeper into the universe, new discoveries may reshape our knowledge and utilization of materials, highlighting the infinite possibilities that lie beyond our world.
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoIconic Sand Dollar Social Club Listed for $3 Million in Folly Beach
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoAfghan Refugee Detained by ICE After Asylum Hearing in New York
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoPeptilogics Secures $78 Million to Combat Prosthetic Joint Infections
-

 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoResearchers Achieve Fastest Genome Sequencing in Under Four Hours
-

 Lifestyle1 week ago
Lifestyle1 week agoJump for Good: San Clemente Pier Fundraiser Allows Legal Leaps
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoResearcher Uncovers Zika Virus Pathway to Placenta Using Nanotubes
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoUS Passport Ranks Drop Out of Top 10 for First Time Ever
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoSan Jose High-Rise Faces Foreclosure Over $182.5 Million Loan
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoJennifer Lopez Addresses A-Rod Split in Candid Interview
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoRegional Pilots’ Salaries Surge to Six Figures in 2025
-
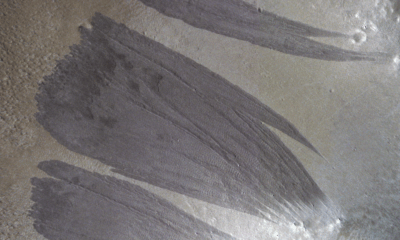
 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoMars Observed: Detailed Imaging Reveals Dust Avalanche Dynamics
-

 Top Stories1 week ago
Top Stories1 week agoChicago Symphony Orchestra Dazzles with Berlioz Under Mäkelä