Health
CDC Revises Hepatitis B Vaccination Guidelines for Infants

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has revised its recommendations regarding the Hepatitis B vaccine for infants. The agency will no longer advise that all newborns receive their first dose within 24 hours of birth. This significant change, approved by the CDC’s Vaccine Advisory Committee in June 2023, has sparked considerable debate among healthcare professionals and public health advocates.
The updated guidelines suggest that the vaccine should still be administered at an appropriate time but do not mandate that it be given immediately after birth. This decision marks a departure from long-standing practices aimed at preventing Hepatitis B transmission from infected mothers to their infants. The CDC’s revision aims to provide more flexibility for healthcare providers while addressing concerns about potential over-vaccination.
Critics of the change have expressed their apprehensions, arguing that delaying the vaccine could put infants at risk. Hepatitis B is a viral infection that can cause severe liver disease and is particularly dangerous for infants, who are more susceptible to its complications. According to the CDC, about 1,800 infants in the United States are born each year to mothers infected with the virus, highlighting the importance of timely vaccination.
In support of the new guidelines, the CDC noted that extensive research has shown that the risk of transmission can be effectively managed through other means, including maternal screening and follow-up care. The agency emphasized that healthcare providers should continue to assess the best vaccination schedule for each individual infant, taking into account their specific circumstances.
The response from the medical community has been mixed. Some pediatricians support the change, believing it allows for a more personalized approach to vaccination. Others argue that the previous recommendation was crucial for safeguarding the health of the most vulnerable populations. This ongoing debate underscores the complexity of immunization strategies and the need for continuous evaluation of public health policies.
The CDC has urged healthcare providers to remain vigilant in monitoring Hepatitis B cases and to educate parents about the importance of vaccination. The agency maintains that its updated guidelines will not diminish the overall effectiveness of the vaccination program against Hepatitis B. It hopes to strike a balance between flexibility and protection, ultimately aiming to reduce the incidence of the virus among infants.
As this new recommendation takes effect, the CDC will continue to collect data and assess the impact of the changes on public health outcomes. The agency remains committed to ensuring that all infants receive necessary vaccinations while adapting to evolving healthcare landscapes. The implications of this change will likely be closely observed by healthcare professionals, parents, and policymakers in the coming months.
-

 Lifestyle1 week ago
Lifestyle1 week agoSend Holiday Parcels for £1.99 with New Comparison Service
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Leads $25M AI Project to Monitor Natural Disasters
-
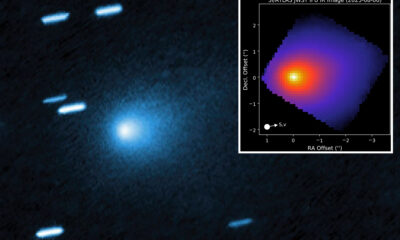
 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoInterstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Emits Unique Metal Alloy, Says Scientist
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoResearchers Achieve Fastest Genome Sequencing in Under Four Hours
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoIconic Sand Dollar Social Club Listed for $3 Million in Folly Beach
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoAfghan Refugee Detained by ICE After Asylum Hearing in New York
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoMcEwen Inc. Secures Tartan Lake Gold Mine Through Acquisition
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoPeptilogics Secures $78 Million to Combat Prosthetic Joint Infections
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoJump for Good: San Clemente Pier Fundraiser Allows Legal Leaps
-
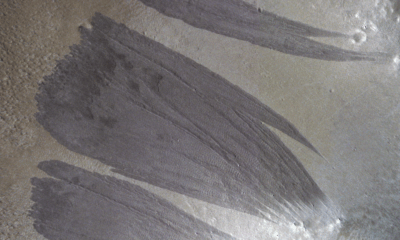
 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoMars Observed: Detailed Imaging Reveals Dust Avalanche Dynamics
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoResearcher Uncovers Zika Virus Pathway to Placenta Using Nanotubes
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoJennifer Lopez Addresses A-Rod Split in Candid Interview