Health
New Study Links Obesity and Inflammation to Lung Aging Risks
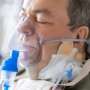
A recent study conducted in Brazil has revealed significant connections between obesity, inflammation, and premature lung aging. The research, involving nearly 900 participants under the age of 40, highlights that factors beyond smoking, such as obesity and systemic inflammation, may contribute to the accelerated aging of the lungs. This finding raises concerns over the potential increase in the risk of developing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
The study underscores the multifaceted nature of lung health, suggesting that lifestyle factors play a crucial role in respiratory conditions. While smoking has long been established as a primary risk factor for lung aging, this research indicates that obesity and inflammation can also have detrimental effects. The results prompt a reevaluation of preventive measures and public health strategies aimed at reducing the burden of COPD.
According to the findings published in the journal *Respiratory Research*, obesity was shown to be a significant factor in lung function decline. Participants with higher body mass indexes (BMIs) demonstrated lower lung function compared to their healthier counterparts. Inflammation, as indicated by elevated levels of inflammatory markers, was also linked to reduced lung capacity. These connections suggest that addressing obesity and inflammation may be essential for maintaining lung health.
The implications of this research extend beyond individual health. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, affecting millions of individuals. In 2020, COPD accounted for approximately 3.23 million deaths, according to the World Health Organization. The rising prevalence of obesity further complicates this issue, as it is associated with various chronic conditions that can exacerbate lung health problems.
Public health officials emphasize the need for comprehensive strategies that address lifestyle factors contributing to respiratory diseases. Initiatives promoting healthy eating, regular physical activity, and awareness of inflammation could play a pivotal role in mitigating the risks associated with COPD.
As healthcare systems grapple with the increasing burden of chronic diseases, the findings from this Brazilian study could inform future research and intervention efforts. By targeting obesity and inflammation, it may be possible to enhance lung health and reduce the incidence of COPD, ultimately improving the quality of life for many individuals.
In summary, the Brazilian study serves as a critical reminder of the interplay between lifestyle factors and lung health. As researchers continue to explore these connections, it becomes increasingly important for individuals and healthcare providers to prioritize the management of obesity and inflammation to safeguard respiratory health.
-

 Lifestyle1 week ago
Lifestyle1 week agoSend Holiday Parcels for £1.99 with New Comparison Service
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Leads $25M AI Project to Monitor Natural Disasters
-
 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoInterstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Emits Unique Metal Alloy, Says Scientist
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoResearchers Achieve Fastest Genome Sequencing in Under Four Hours
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoIconic Sand Dollar Social Club Listed for $3 Million in Folly Beach
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoAfghan Refugee Detained by ICE After Asylum Hearing in New York
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoMcEwen Inc. Secures Tartan Lake Gold Mine Through Acquisition
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoPeptilogics Secures $78 Million to Combat Prosthetic Joint Infections
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoJump for Good: San Clemente Pier Fundraiser Allows Legal Leaps
-
 Science2 months ago
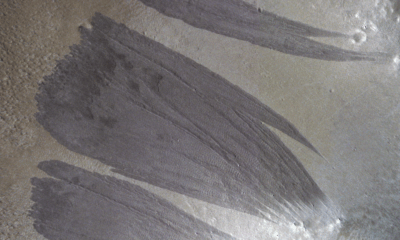
Science2 months agoMars Observed: Detailed Imaging Reveals Dust Avalanche Dynamics
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoResearcher Uncovers Zika Virus Pathway to Placenta Using Nanotubes
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoJennifer Lopez Addresses A-Rod Split in Candid Interview