Science
Researchers Develop Artificial Proteins for Advanced Energy Storage
A team of researchers has successfully engineered a class of proteins capable of transporting and storing electricity, paving the way for innovative energy storage solutions. The study, led by Aitziber L. Cortajarena, Reyes Calvo, and Maica Morant, reveals how these modified proteins can be utilized to create sustainable and biocompatible conducting materials. The findings were published in the journal Advanced Materials and are part of the ongoing e-PROT project.
The proteins developed in this research consist of small, repeated units assembled like LEGO bricks. Each unit shares a consistent shape, and when combined, they form a larger, stable, and modular structure. This unique architecture allows for specific functionalities to be added without compromising the overall integrity of the material. The researchers aimed to enhance the proteins’ ability to conduct electricity efficiently. To achieve this, they used genetic modifications to alter the DNA responsible for protein production.
The implications of this research extend beyond theoretical applications. The modified proteins demonstrate enhanced ionic conductivity, allowing for quick energy storage and release. This breakthrough means that these protein-based materials could potentially replace traditional conductive materials found in batteries and supercapacitors, making energy storage devices safer for human use.
Juan David Cortés, a Pre-PhD researcher at BCMaterials, is investigating the conductivity of films made from these modified proteins. His work plays a critical role in integrating these proteins into energy storage systems, which could revolutionize how electronic devices function.
The future looks promising for energy storage technology. As these conducting proteins are further developed, they may lead to the creation of bioelectronic devices, including pacemakers, implantable glucose sensors, and brain electrodes for treating conditions such as Parkinson’s disease. The study highlights a vision where energy is stored in biodegradable and sustainable materials, making it easier to imagine a world where everyday devices, from smartphones to fitness trackers, operate on environmentally friendly energy sources.
This research not only showcases the potential of artificial proteins in energy applications but also emphasizes a shift towards more sustainable practices in technology. The next generation of energy storage devices based on these innovative materials is on the horizon, bringing with it the promise of a safer and more sustainable future for energy consumption.
-
 Science3 weeks ago
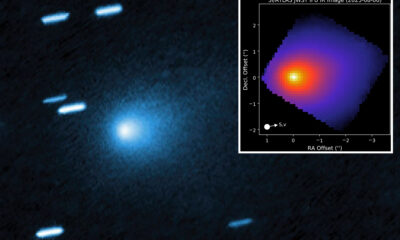
Science3 weeks agoInterstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Emits Unique Metal Alloy, Says Scientist
-

 Politics3 weeks ago
Politics3 weeks agoAfghan Refugee Detained by ICE After Asylum Hearing in New York
-

 Business3 weeks ago
Business3 weeks agoIconic Sand Dollar Social Club Listed for $3 Million in Folly Beach
-

 Health3 weeks ago
Health3 weeks agoPeptilogics Secures $78 Million to Combat Prosthetic Joint Infections
-

 Science3 weeks ago
Science3 weeks agoResearchers Achieve Fastest Genome Sequencing in Under Four Hours
-

 Lifestyle3 weeks ago
Lifestyle3 weeks agoJump for Good: San Clemente Pier Fundraiser Allows Legal Leaps
-

 Health3 weeks ago
Health3 weeks agoResearcher Uncovers Zika Virus Pathway to Placenta Using Nanotubes
-
 Science3 weeks ago
Science3 weeks agoMars Observed: Detailed Imaging Reveals Dust Avalanche Dynamics
-

 World3 weeks ago
World3 weeks agoUS Passport Ranks Drop Out of Top 10 for First Time Ever
-

 Entertainment3 weeks ago
Entertainment3 weeks agoJennifer Lopez Addresses A-Rod Split in Candid Interview
-

 Business3 weeks ago
Business3 weeks agoSan Jose High-Rise Faces Foreclosure Over $182.5 Million Loan
-

 Top Stories3 weeks ago
Top Stories3 weeks agoChicago Symphony Orchestra Dazzles with Berlioz Under Mäkelä