Science
Machine Learning Unveils Rare Quasars Acting as Gravitational Lenses

A recent breakthrough in astronomical research has revealed that machine learning technology can identify quasars acting as strong gravitational lenses. Quasars, among the brightest objects in the universe, have been cataloged extensively, with nearly 300,000 recorded in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. Yet, only twelve candidates for this unique behavior have been identified, leading to just three confirmed cases thus far.
The significance of these findings is profound. Gravitational lensing occurs when a massive object, such as a quasar, bends the light from objects behind it. This phenomenon allows astronomers to study the mass of the quasar’s host galaxy in detail. Typically, the intense brightness of quasars obscures their surroundings, making it nearly impossible to measure the mass of their host galaxies. The ability to find and confirm these lenses not only enhances our understanding of quasar properties but also contributes to the broader field of cosmology.
Machine learning algorithms have revolutionized the way scientists approach complex data sets. By training models to recognize patterns within vast amounts of astronomical data, researchers have been able to isolate instances of quasar lensing that might have otherwise gone unnoticed. This innovative approach showcases the potential of artificial intelligence in advancing scientific discovery.
The confirmation of these gravitational lensing candidates marks a significant milestone in the ongoing exploration of the universe. Quasars serve as important markers for understanding the distribution of matter in the cosmos. Each confirmed system enhances the ability of astronomers to conduct detailed studies, ultimately leading to a more comprehensive understanding of the universe’s structure and evolution.
As this field continues to evolve, the integration of machine learning with traditional astronomical techniques promises to uncover further rare phenomena. Researchers are optimistic that with continued advancements in technology, more quasars exhibiting gravitational lensing will be identified. The implications of such discoveries could reshape our understanding of both quasars and the galaxies that host them.
In summary, the identification of quasars acting as gravitational lenses through machine learning is a remarkable advancement in astronomy. With only a handful of confirmed cases, these systems offer valuable insights into the dynamics of the universe, bridging gaps in knowledge that have persisted for decades. The partnership between technology and astronomy continues to yield fruitful results, paving the way for future discoveries that will deepen our understanding of the cosmos.
-
 Science1 month ago
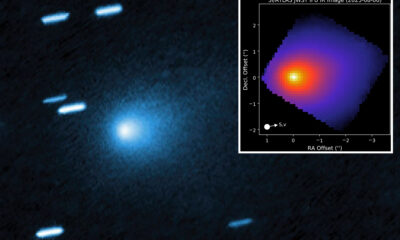
Science1 month agoInterstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Emits Unique Metal Alloy, Says Scientist
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoResearchers Achieve Fastest Genome Sequencing in Under Four Hours
-

 Politics1 month ago
Politics1 month agoAfghan Refugee Detained by ICE After Asylum Hearing in New York
-

 Business1 month ago
Business1 month agoIconic Sand Dollar Social Club Listed for $3 Million in Folly Beach
-

 Health1 month ago
Health1 month agoPeptilogics Secures $78 Million to Combat Prosthetic Joint Infections
-

 Business1 month ago
Business1 month agoMcEwen Inc. Secures Tartan Lake Gold Mine Through Acquisition
-

 Lifestyle1 month ago
Lifestyle1 month agoJump for Good: San Clemente Pier Fundraiser Allows Legal Leaps
-
 Science1 month ago
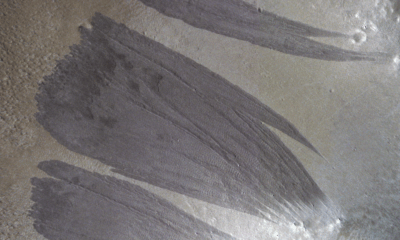
Science1 month agoMars Observed: Detailed Imaging Reveals Dust Avalanche Dynamics
-

 Health1 month ago
Health1 month agoResearcher Uncovers Zika Virus Pathway to Placenta Using Nanotubes
-

 World1 month ago
World1 month agoUS Passport Ranks Drop Out of Top 10 for First Time Ever
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Leads $25M AI Project to Monitor Natural Disasters
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoJennifer Lopez Addresses A-Rod Split in Candid Interview