Health
Study Reveals Genetic Links Between Roommates and Gut Bacteria

Research published in Nature Communications has uncovered intriguing connections between genetics and gut bacteria, suggesting that the genetic makeup of individuals can influence the microbial environment within shared living spaces. This study, conducted on rats, highlights the potential impact of genetic factors on the gut microbiome, revealing that these effects may extend beyond individual hosts to their social groups.
The researchers observed that the gut microbiota of rats living together showed significant similarities, which could be attributed to their genetic backgrounds. Specifically, the study found that the genetic traits of one rat could affect the types of bacteria residing in the intestines of its cage mate. This phenomenon indicates a complex interplay between genetics and microbial communities, as the bacteria in the gut are known to play crucial roles in health and disease.
Understanding how genetic influences can ripple through social groups opens new avenues for exploring the relationship between genetics, health, and the microbiome. The implications of this research could be profound, as it suggests that social interactions and shared environments might shape individual health outcomes through microbial transmission.
In this study, the researchers utilized a controlled environment to monitor rat interactions, allowing for precise observations of how genetic similarities influenced gut bacterial composition. The findings suggest that when individuals share close quarters, they may also share microbial communities, which could potentially affect their overall health.
The significance of this study lies not only in its implications for animal research but also for human health. As scientists continue to explore the connections between genetics and the microbiome, this research may pave the way for future studies on how living arrangements, social connections, and even family ties could impact health through shared microbial exposure.
As further research is conducted, the relationship between genetic factors and gut microbiota will likely become clearer, emphasizing the importance of considering both genetics and environment in health studies. This work underscores the need for a holistic approach to health that takes into account the interconnectedness of individuals within their social and microbial environments.
The study contributes to a growing body of evidence that suggests our health is not determined solely by our genetic code but also by the intricate web of interactions among the microbes that inhabit our bodies and those of those around us. Understanding these dynamics could lead to innovative approaches to health maintenance and disease prevention, particularly in communal living settings such as shared housing and nursing homes.
Future research will need to explore the practical applications of these findings, particularly how they may inform strategies for improving gut health and overall well-being. As global interest in the microbiome continues to rise, studies like this will be essential in unraveling the complex relationships that define human health.
-

 Lifestyle1 week ago
Lifestyle1 week agoSend Holiday Parcels for £1.99 with New Comparison Service
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Leads $25M AI Project to Monitor Natural Disasters
-
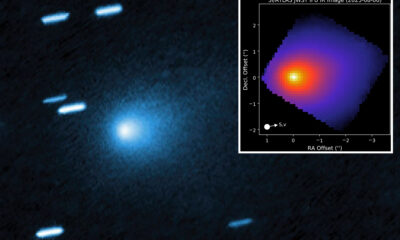
 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoInterstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Emits Unique Metal Alloy, Says Scientist
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoResearchers Achieve Fastest Genome Sequencing in Under Four Hours
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoIconic Sand Dollar Social Club Listed for $3 Million in Folly Beach
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoAfghan Refugee Detained by ICE After Asylum Hearing in New York
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoMcEwen Inc. Secures Tartan Lake Gold Mine Through Acquisition
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoPeptilogics Secures $78 Million to Combat Prosthetic Joint Infections
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoJump for Good: San Clemente Pier Fundraiser Allows Legal Leaps
-
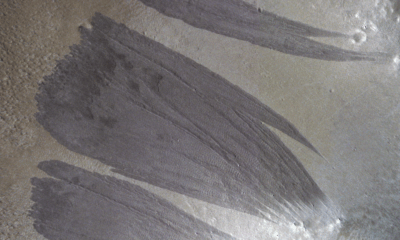
 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoMars Observed: Detailed Imaging Reveals Dust Avalanche Dynamics
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoResearcher Uncovers Zika Virus Pathway to Placenta Using Nanotubes
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoJennifer Lopez Addresses A-Rod Split in Candid Interview